Single celled life
Most life on Earth is unicellular
The first life forms were unicellular and the last universal common ancestor of all life was unicellular
Prokaryotes:
Prokaryotes don't have any organellesNo membrane aside from the cell membrane and are all unicellular
They have plasma membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, DNA
DNA is in the form of rings called plasmids
These are the oldest life with fossils around 3.5 billion years ago
Archaea:
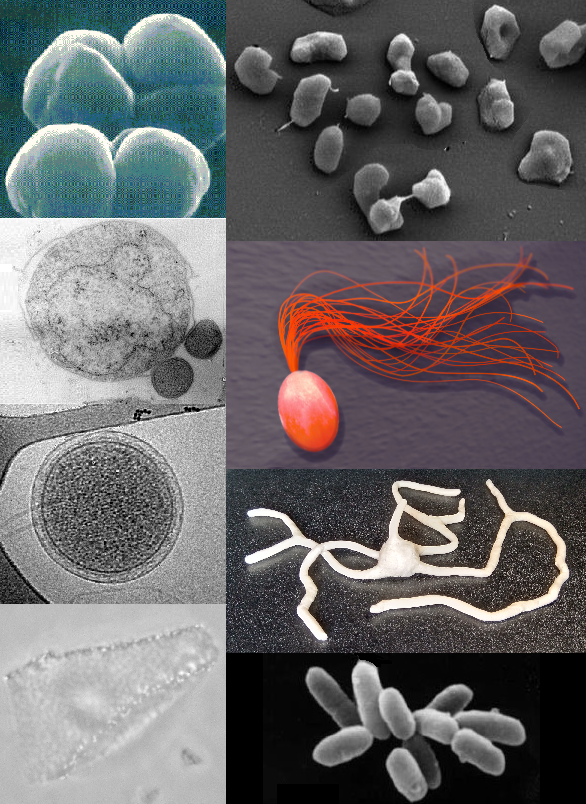
They are prokaryotic organisms in the domain archaea
They are thought to be the oldest lifeProkaryotes have similar morphologies so it is hard to tell them apart in fossils
Methanogens:
Archaea that are present in mud, swamps, intestinesThey derive energy from H2 and CO2 and emit methane as a waste product
Bacteria:
They are prokaryotic organisms in the domain bacteria
They are less archaic than archaea but they have existed for 3 billion years
They makeup most prokaryotes in modern times
They are very quick to adapt to changes
A strain of bacteria can pass its genes to other strains of bacteria, this is called horizontal gene transfer
Gram positive bacteria:
Bacteria ith thick cell membranes
The largest division of gram positive bacteria is the proteobacteria
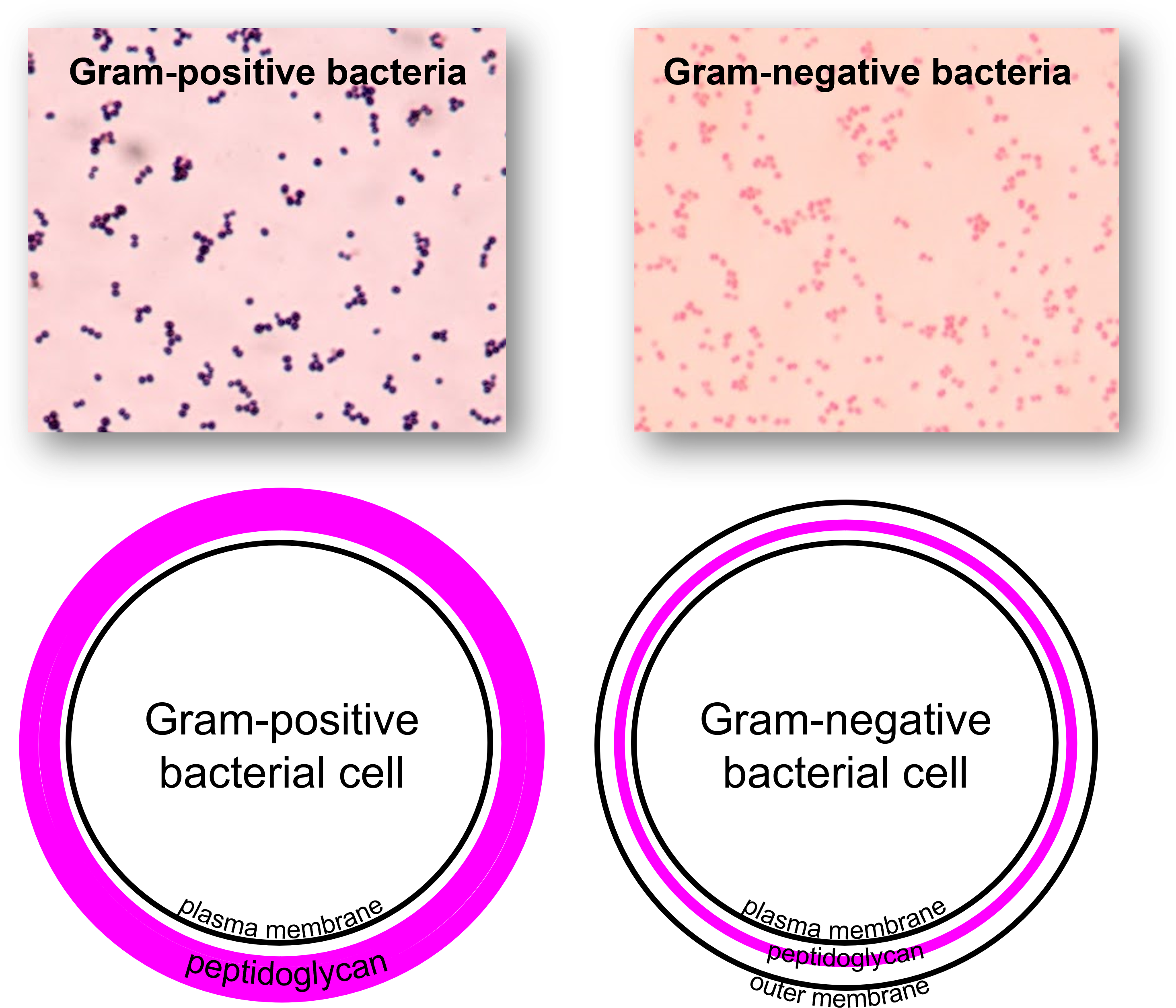
Gram negative bacteria:
Bacteria with thinner cell membranes
Cyanobacteria:
Cyanobacteria are gram negative bacteria that can use photosynthesis
They are an important part of aquatic food webs
Spirochetes:
Spirochetes are a phylum of gram negative bacteria that contain a double membrane and are mostly corkscrew shaped
Lime disease and syphilis are caused by bacteria of this phylum
Chlamydia:
Genus of gram negative bacteria that are strictly parasitic and live in animal cells
The disease chlamydia is caused a member of this genus
Extremophiles:
Some organisms survive and thrive in extreme conditions, they are called extremophiles
Thermophiles:
Extremophiles that can live in very hot temperatures
They have adaptations that allow their proteins to stay stable in extremely hot temperatures
Ex: Pyrolobus fumarii is a species of archaea that live in hydrothermal vents at temperatures around 113°C
Halophiles:
Extremophiles that live in very slaty environments like the dead sea
Most breathe oxygen and are heterotrophs but some haloarchaea can use light to make food
This process is unrelated to photosynthesis as they don't harvest carbon from the atmosphere
Protista:
They are eukaryotic organisms in the domain eukarya and kingdom protista
Some protists are more closely related to animals/plants/fungi than other protists
They are mostly unicellular but some are multicellular and some even reproduce asexually
They need to live in moist areas
There are mainly 3 types of protists,
Protozoa:
Protists that are animal-like
They are heterotrophs
They use either cilia or flagella to move or move like amoeba
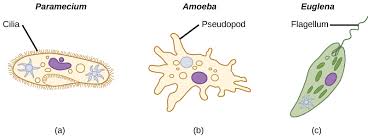
Amoeba are protozoa that use pseudopodia to move
Malaria is caused by a protozoa called plasmodium vivax
Algae:
Protists that are plant-like
All algae photosynthesize similar to plants but use different types of chlorophyll
Algae are generally divided into green algae, red algae and brown algae
Sea weed are multicellular algae
Green algae:
Sailor's eyeball, the largest unicellular organism, is a green algae
It lives on the sea floor and can grow to 5cm across

Land plants are thought to have evolved from the same ancestor as green algae
They are the most abundant and diverse form of algae and have chloroplasts like plants
Green algae live in shallow waters
Red algae:
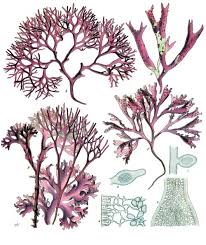
They can live in deeper waters
They have a pigment called phycoerythrin which makes the chlorophyll better in deeper water compared to green algae
Brown algae:

Most seaweedIncluding kelp are brown algae
All known brown algae are multicellular
They are the largest and most complex of all multicellular algae
Fungus like protist:
Protists that are fungi-like
They absorbs nutrients from dead and decaying organisms and have hyphae like structures
These include slime molds
Slime molds:
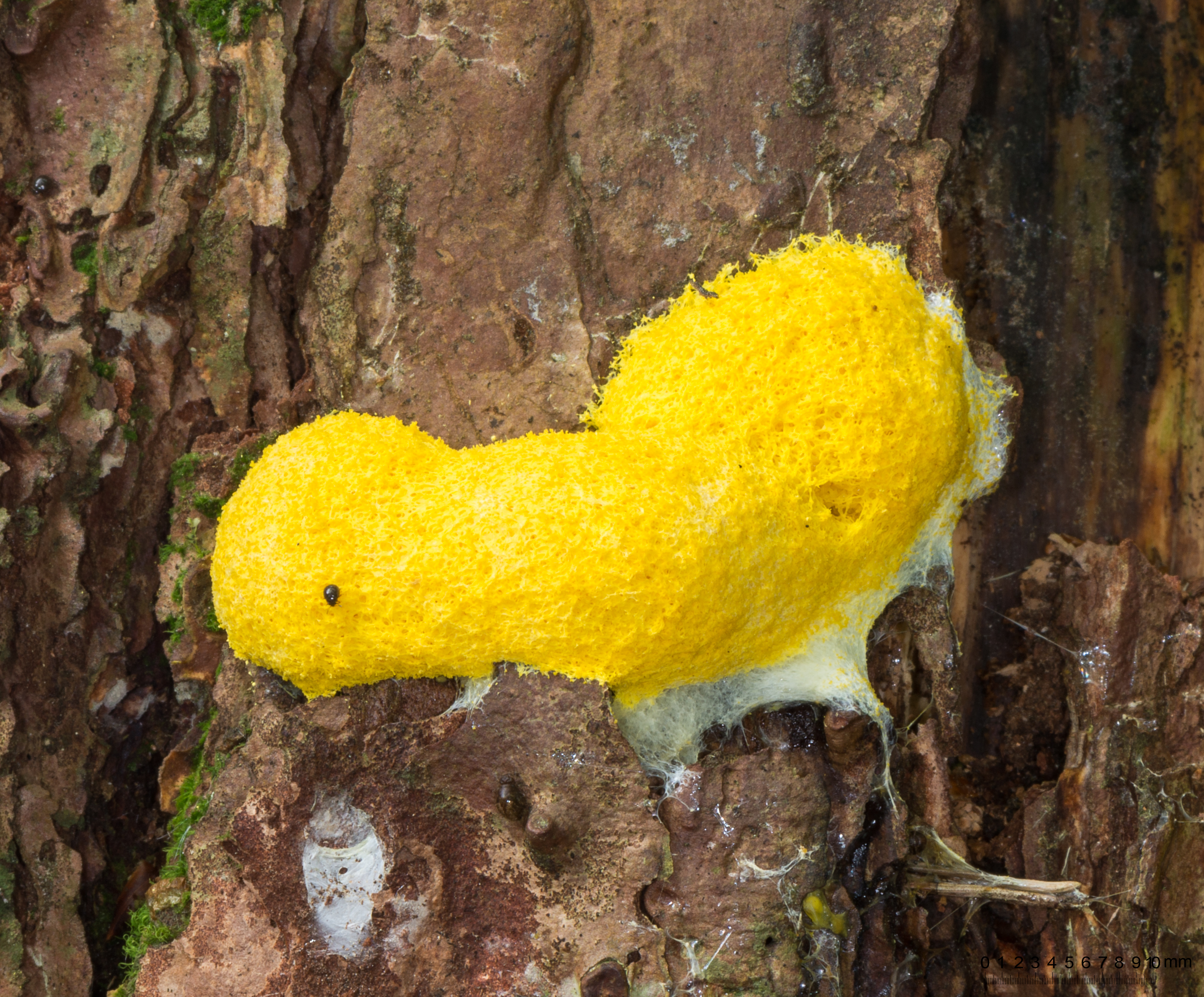

They can move around similar to amoeba and eat bacteria through phagocytosis
They are often brightly colored and near microscopic in size




